Rich Polk/NBC via Getty Images Video footage of an accident that occurred on the set of an Eddie Murphy movie...
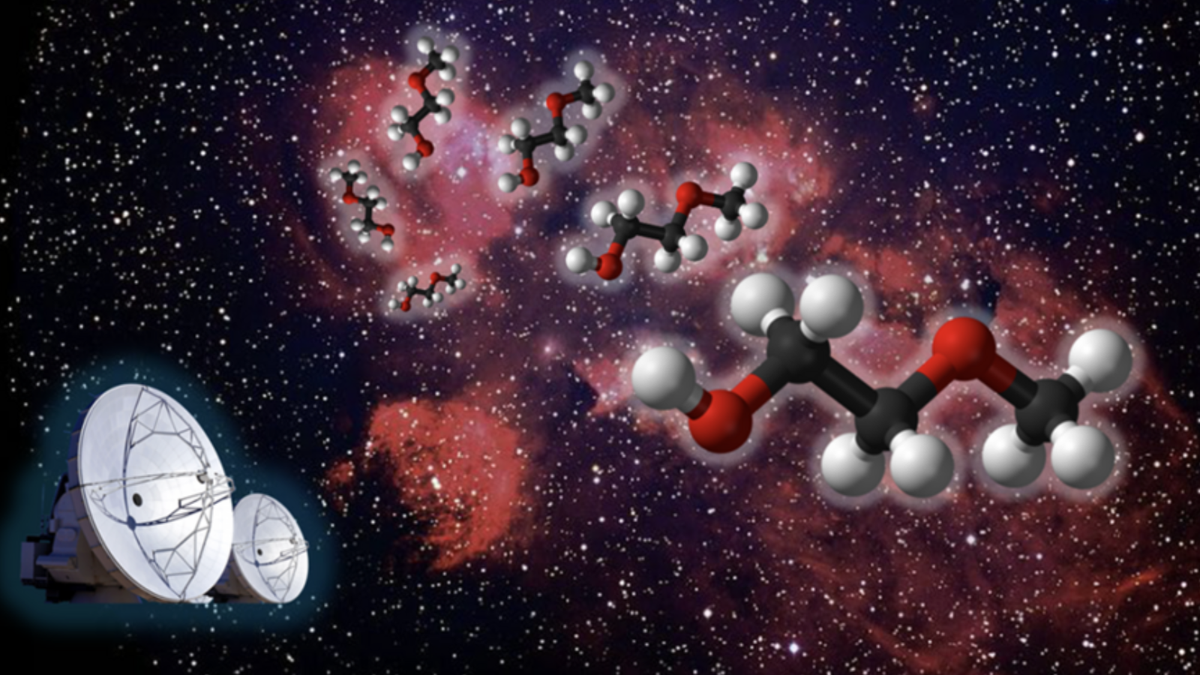
Scientists have discovered a hitherto unknown space particle while examining a region relatively close to condensed star birth, a cosmic...
It's good that Wednesday's press conference began with prayer.The Chicago Bears will likely need some divine intervention to pull off...
There are few video game marketing terms more obscure than "early access." What's even more painful is that it can...
WASHINGTON (AP) — When Pres Joe Biden Show his status during a Campaign stop at a public golf course And...
According to the Washington Post, the former president was not charged but was named as an unindicted conspirator. The US...
the Arsenal The lottery jackpot continues to grow after no one matched all six numbers from Monday night's drawing.Get your...
celebrities by Maude Campbell published April 24, 2024 Updated April 24, 2024, 4:19 PM ET This American will be looking...
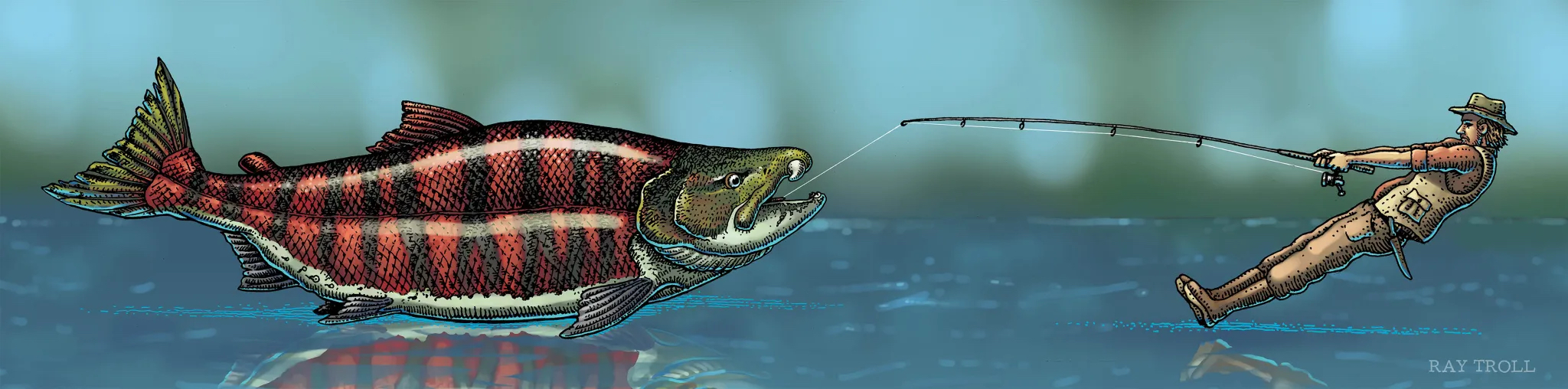
In 1964, paleontologists discovered the skull of a giant salmon ancestor in a quarry near the town of Gateway, Oregon....
It's hard to say exactly when Alexander Georgiev really started to win some hearts and change some minds on Tuesday...