Animation of the European Space Agency’s Solar Orbiter. Credit: ESA/Medialab
The latest Solar Orbiter images show the full sun in unprecedented detail. It was taken on March 7, 2022, when the spacecraft was transiting directly between the Earth and the Sun.
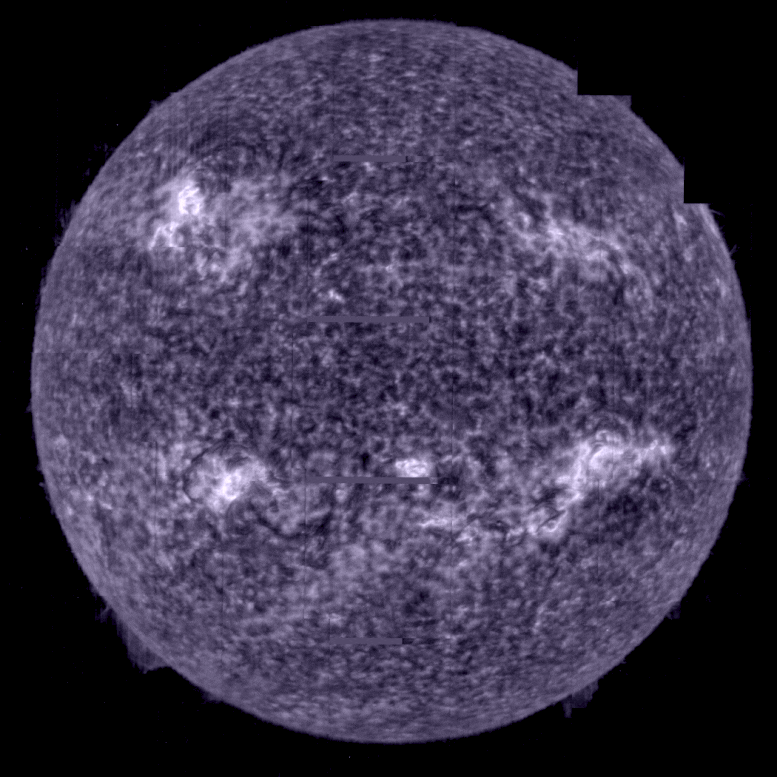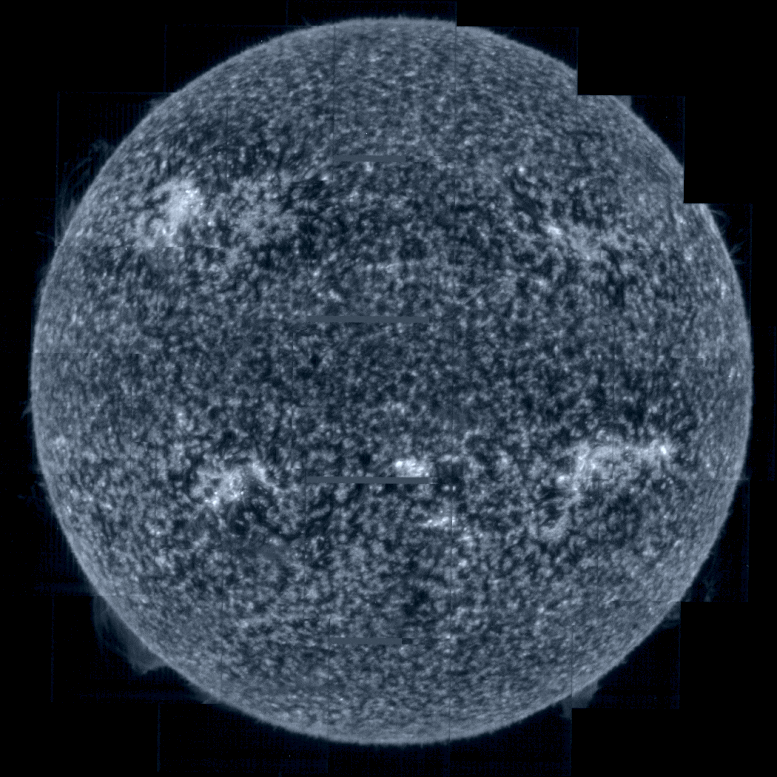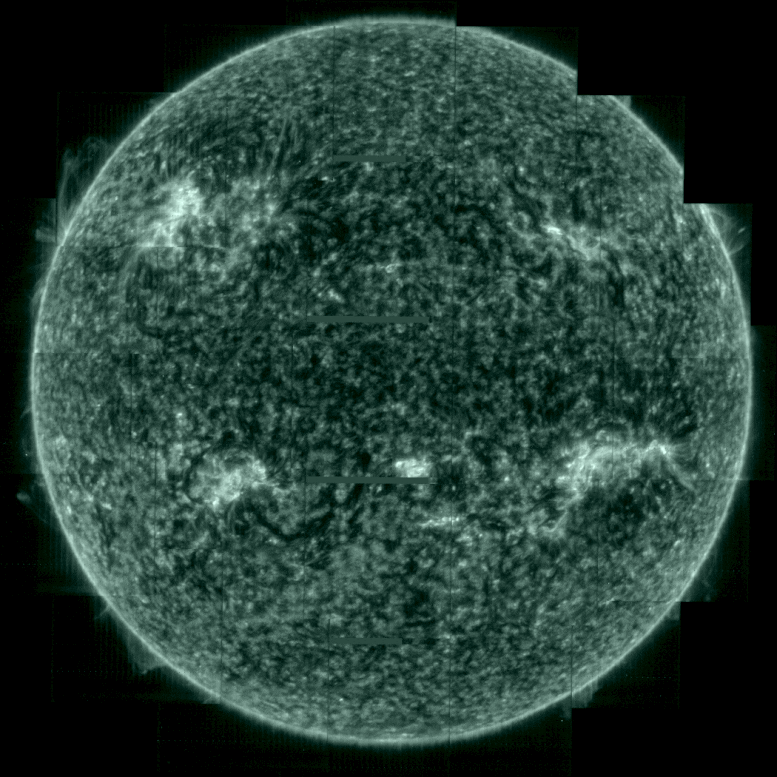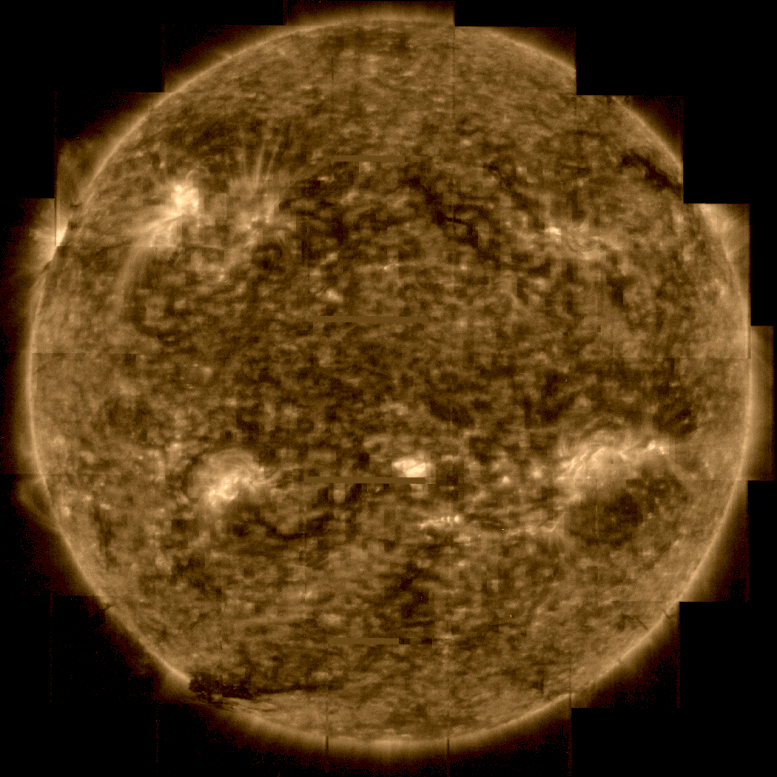
One of the images captured by the Extreme Ultraviolet Imager (EUI) is the highest-resolution image of the full sun’s disk and outer atmosphere, the corona, ever taken.
Another image taken by the Spectral Imaging of the Coronal Environment (SPICE) instrument represents the first complete image of the Sun in 50 years, and the best image taken along the Lyman beta wavelength of ultraviolet radiation emitted by hydrogen gas.
The images were taken when the solar orbiter was about 75 million kilometers away, halfway between our world and its parent star. EUI’s high-resolution telescope captures images with such a high spatial resolution that, at that close distance, a mosaic of 25 individual images is required to cover the entire Sun. Taken one by one, the full image was taken over a period of over four hours because each piece takes about 10 minutes, including the time it takes the spacecraft to point from one part to the next.
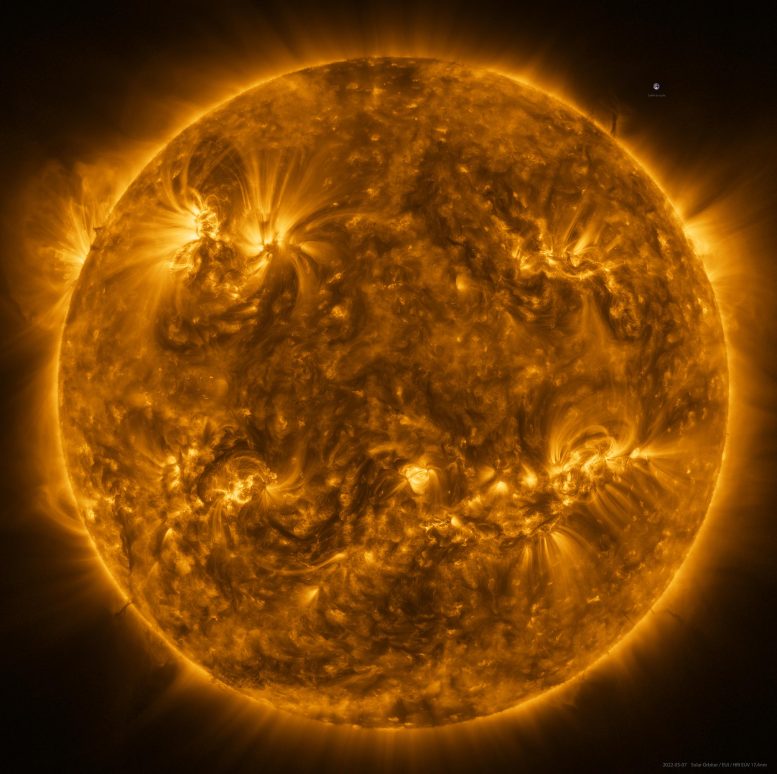

The Sun as seen by the Solar Orbiter in extreme ultraviolet light from a distance of approximately 75 million km. The image is a mosaic of 25 individual images taken on March 7, 2022 by the Ultraviolet Imaging Instrument (EUI) High Resolution Telescope. This image was taken at a wavelength of 17 nanometers, in the extreme ultraviolet region of the electromagnetic spectrum, revealing the sun’s upper atmosphere, the corona, which has a temperature of about one million degrees Celsius. An Earth image of the scale at the 2 o’clock position is also included. Credit: ESA and NASA/Solar Orbiter/EUI Team; Data processing: E. Kraaikamp (ROB)
In total, the final image It contains more than 83 million pixels in a grid of 9148 x 9112 pixels. For comparison, this image has a resolution ten times better than what a 4K TV screen can display.
EUI depicts the Sun at a wavelength of 17 nanometers, in the extreme ultraviolet region of the electromagnetic spectrum. This reveals the sun’s upper atmosphere, the corona, which has a temperature of about a million degrees[{” attribute=””>Celsius.
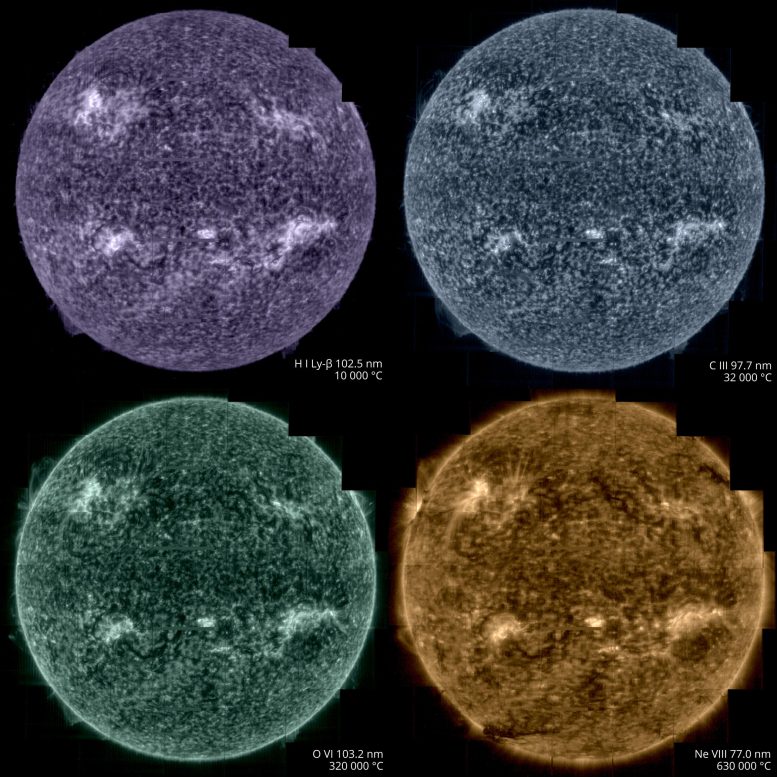
Solar Orbiter took images of the Sun on March 7, from a distance of roughly 75 million kilometres, using its Spectral Imaging of the Coronal Environment (SPICE) instrument. SPICE takes simultaneous “spectral images” at several different wavelengths of the extreme ultraviolet spectrum by scanning its spectrometer slit across a region on the Sun. The different wavelengths recorded correspond to different layers in the Sun’s lower atmosphere. Purple corresponds to hydrogen gas at a temperature of 10,000°C, blue to carbon at 32,000°C, green to oxygen at 320,000°C, yellow to neon at 630,000°C. Each full-Sun image is made up of a mosaic of 25 individual scans. It represents the best full Sun image taken at the Lyman beta wavelength of ultraviolet light that is emitted by hydrogen gas. Credit: ESA & NASA/Solar Orbiter/SPICE team; Data processing: G. Pelouze (IAS)
At the 2 o’clock (near the image of the Earth for scale) and 8 o’clock positions on the edges of the Sun, dark filaments can be seen projecting away from the surface. These ‘prominences’ are prone to erupt, throwing huge quantities of coronal gas into space and creating ‘space weather’ storms.
In addition to EUI, the SPICE instrument was also recording data during the crossing. These too needed to be pieced together as a mosaic.
SPICE is designed to trace the layers in the Sun’s atmosphere from the corona, down to a layer known as the chromosphere, getting closer to the surface. The instrument does this by looking at the different wavelengths of extreme ultraviolet light that come from different atoms.
Taking the Sun’s temperature. Credit: ESA & NASA/Solar Orbiter/SPICE team; Data processing: G. Pelouze (IAS)
In the SPICE sequence of images purple corresponds to hydrogen gas at a temperature of 10,000°C, blue to carbon at 32,000°C, green to oxygen at 320,000°C, yellow to neon at 630,000°C.
This will allow solar physicists to trace the extraordinarily powerful eruptions that take place in the corona down through the lower atmospheric layers. It will also allow them to study one of the most puzzling observations about the Sun: how the temperature is rising through the ascending atmospheric layers.
Usually the temperature drops as you move away from a hot object. But above the Sun, the corona reaches a million degrees Celsius whereas the surface is only about 5000°C. Investigating this mystery is one of the key scientific objectives of Solar Orbiter.
The images were taken on 7 March, precisely when Solar Orbiter crossed the Sun-Earth line, so the images can be compared with Earth-bound solar instruments and cross-calibrated. This will make it easier to compare results from different instruments and observatories in future.
On March 26, Solar Orbiter reaches another mission milestone: its first close perihelion. The spacecraft is now inside the orbit of Mercury, the inner planet, taking the highest resolution images of the Sun it can take. It is also recording data on the solar wind of particles that flows outwards from the Sun.
And this is just the start, over the coming years the spacecraft will repeatedly fly this close to the Sun. It will also gradually raise its orientation to view the Sun’s previously unobserved polar regions.
Solar Orbiter is a space mission of international collaboration between ESA and NASA.




/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25550621/voultar_snes2.jpg)


More Stories
Watch a Massive X-Class Solar Explosion From a Sunspot Facing Earth (Video)
New Study Challenges Mantle Oxidation Theory
The theory says that complex life on Earth may be much older than previously thought.